Dr. Perez minimal invasive total joint replace
Dr. Perez minimal invasive total joint replace
Dr. Perez minimal invasive total joint replace
Dr. Perez minimal invasive total joint replace
Another total joint replacement done in Victoria not by us
Knee Anatomy/Function
Anatomy and function of the knee
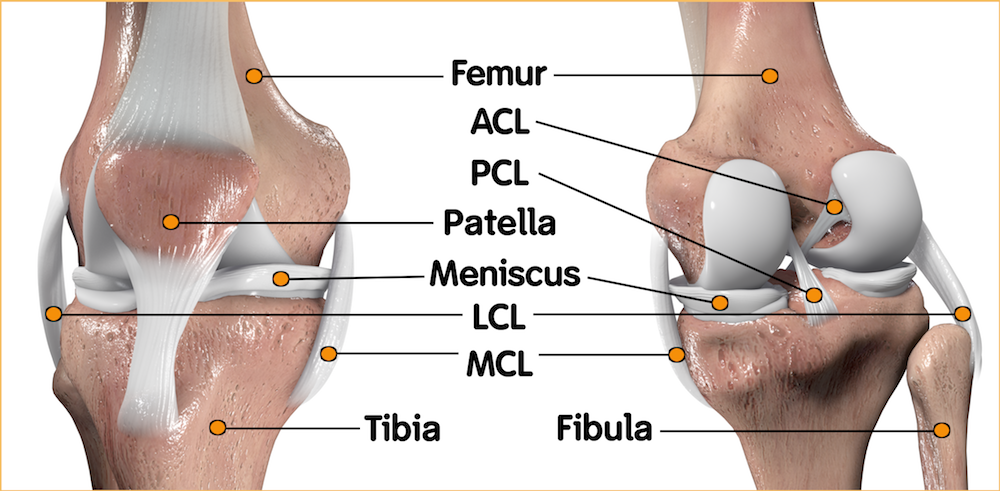
What makes up your knee?
The knee joint is the point at which the femur bone of the thigh meets the tibia bone of the lower leg. All the components of the knee - bones, cartilage, synovial membrane, ligaments, tendons and muscles - must work together properly for the knee to move smoothly.
Cartilage is a protective cushioning that keeps the bones from rubbing against one another.
In a healthy knee, a thin, smooth tissue liner called the synovial membrane releases a fluid that lubricates the knee, reducing friction as the bones move.
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved
Knee Arthritis
What is knee arthritis?

What is arthritis of the knee?
Arthritis of the knee is a disease which wears away the cartilage between the femur (thigh bone) and the tibia (shin bone) causing the two bones to scrape against each other, raw bone on raw bone. When this happens, the joint becomes pitted, eroded and uneven. The result is pain, stiffness and instability. In some cases, motion of the leg may be greatly restricted.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, which is the most common form of arthritis in the United States, is degenerative and, although it most often occurs in patients over the age of 50, it can occur at any age, especially if the joint is in some way damaged.
It is usually confined to the large weight-bearing joints of the lower extremities, including the hips and knees, but may affect the spine and upper extremity joints, too. Patients with osteoarthritis often develop large bone spurs, or osteophytes, around the joint, further limiting motion.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Unlike osteoarthritis, which is a "wear and tear" phenomenon, rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disease that results in joint pain, stiffness and swelling. The disease process leads to severe, and at times rapid, deterioration of multiple joints, resulting in severe pain and loss of function.
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved
What is Partial Knee Replacement
Partial knee implant 
The partial knee replacement surgical procedure allows your surgeon to access, remove and accurately replace only the damaged surface of your knee - leaving your healthy bone intact. Below is a brief description of the procedure:
Post-operative protocol
After leaving the operating room, you will most likely be transported to a recovery area where you will be closely monitored before returning to your room. Once you have returned to your room and your surgeon has given approval, you may begin the post-operative rehabilitation process. Your surgeon may recommend the following to begin rehabilitation while you are still in the hospital:
What to expect
Important safety notes
Individual results of joint replacement vary. Implants are intended to relieve knee pain and improve function, but may not produce the same feel or function as your original knee. There are potential risks with knee replacement surgery such as loosening, wear and infection that may result in the need for additional surgery. Patients should not perform high impact activities such as running and jumping unless their surgeon tells them that the bone has healed and these activities are acceptable. Early device failure, breakage or loosening may occur if a surgeon's limitations on activity level are not followed.
Talk to your doctor to determine what treatment may be best for you.
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved

The partial knee replacement surgical procedure allows your surgeon to access, remove and accurately replace only the damaged surface of your knee - leaving your healthy bone intact. Below is a brief description of the procedure:
- An incision is made to expose the damaged joint
- For a Uni knee implant, the end of the femur and top of the tibia are shaped to accommodate the Uni implant components
- Trial components are placed to ensure proper alignment
- Once properly aligned, the trial components are removed
- The final implant components are implanted
- The incision is closed.
For a PFJ implant, only the front surface of the femur is shaped to accommodate the PFJ implant component
Post-operative protocol
After leaving the operating room, you will most likely be transported to a recovery area where you will be closely monitored before returning to your room. Once you have returned to your room and your surgeon has given approval, you may begin the post-operative rehabilitation process. Your surgeon may recommend the following to begin rehabilitation while you are still in the hospital:
- Ice and elevation to reduce pain and swelling in your knee
- A continuous passive motion machine that will promote the return of your knee's range of motion
- Walking with a walker or crutches on your first day after surgery
What to expect
- On average, this type of surgery takes approximately one to three hours, depending on your individual circumstances.
- Usually you'll be ready to return to your room after one to three hours in recovery.
- After surgery, your pain may be managed via intravenous therapy and/or a pain pump and/or injection and/or pills given by mouth.
- Depending on your situation, you may be able to walk with the aid of a walker or cane the day after surgery.
- It is normal for your joint to remain warm, swollen and slightly tender for a number of weeks. Call your doctor immediately, however, if you notice:
- Increased pain, redness or swelling
- Incision drainage
- Prolonged nausea or vomiting
- Chest pain or shortness of breath
- Tenderness in the calf or thigh of the operated leg
- A fever
- Most patients are ready to drive a car about eight weeks after surgery, but not unless your surgeon authorizes it.
- Recovery varies greatly based on individual factors but most patients resume normal activities in about 12 weeks following surgery.
Important safety notes
Individual results of joint replacement vary. Implants are intended to relieve knee pain and improve function, but may not produce the same feel or function as your original knee. There are potential risks with knee replacement surgery such as loosening, wear and infection that may result in the need for additional surgery. Patients should not perform high impact activities such as running and jumping unless their surgeon tells them that the bone has healed and these activities are acceptable. Early device failure, breakage or loosening may occur if a surgeon's limitations on activity level are not followed.
Talk to your doctor to determine what treatment may be best for you.
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved
What is Total Knee Replacement
Is total knee replacement surgery for you?
If you are considering knee replacement surgery, you have plenty of company. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality reports that more than 600,000 knee replacements are performed each year in the United States.1
Even better news is that the US Department of Health and Human services considers total knee replacement to be one of the most successful and cost effective interventions in medicine. In fact, the success rate for knee replacements 10 years after surgery is 90-95%.1
This surgery is intended for people with severe knee damage, due to injury or to arthritis-related deterioration of the joint. Knee replacement can relieve pain and allow you to be more active. Your doctor may recommend it if you have persistent knee pain, and medicine and other treatments are not helping you anymore.
The decision to have knee replacement surgery should be a cooperative one made by you, your family, your primary care doctor, and your orthopaedic surgeon. The process of making this decision typically begins with a referral by your primary care doctor to an orthopaedic surgeon for an initial evaluation.
How is knee replacement surgery performed?
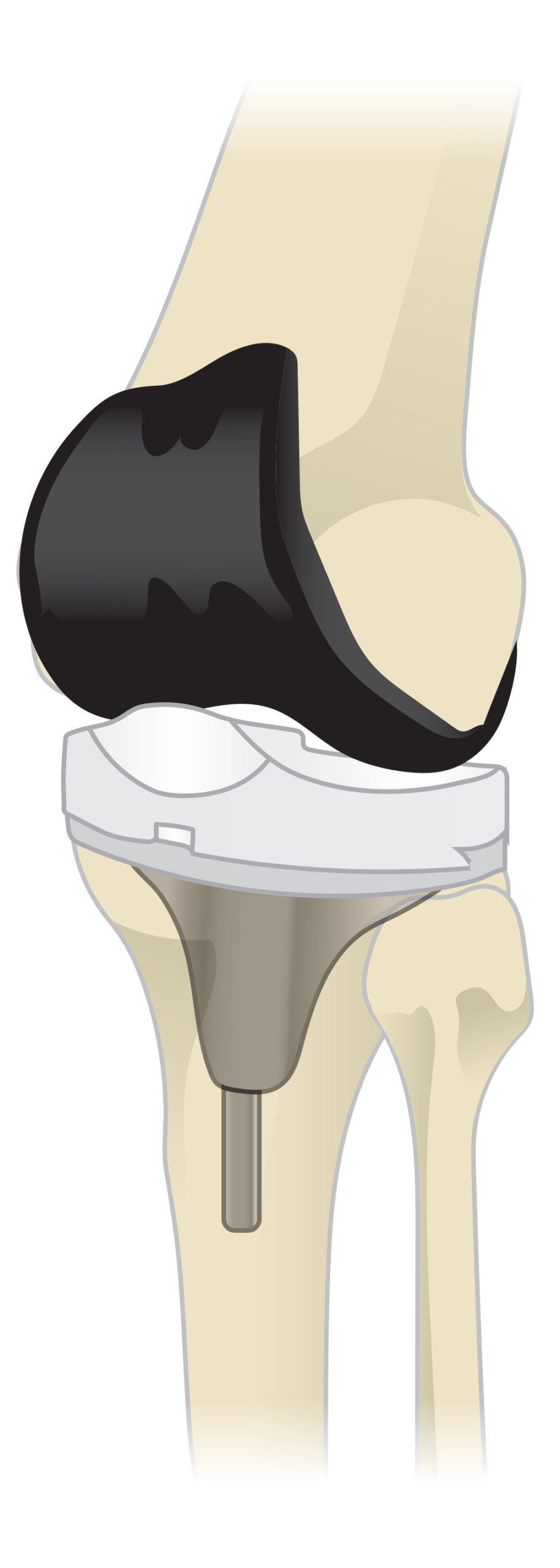
During knee replacement surgery, the surgeon surgically removes the damaged bone and cartilage of the joint and replaces it with smooth, artificial implants - thereby eliminating painful bone-on-bone contact.
Almost all knee replacement implants consist of a four-part system:
References
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved.
If you are considering knee replacement surgery, you have plenty of company. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality reports that more than 600,000 knee replacements are performed each year in the United States.1
Even better news is that the US Department of Health and Human services considers total knee replacement to be one of the most successful and cost effective interventions in medicine. In fact, the success rate for knee replacements 10 years after surgery is 90-95%.1
This surgery is intended for people with severe knee damage, due to injury or to arthritis-related deterioration of the joint. Knee replacement can relieve pain and allow you to be more active. Your doctor may recommend it if you have persistent knee pain, and medicine and other treatments are not helping you anymore.
The decision to have knee replacement surgery should be a cooperative one made by you, your family, your primary care doctor, and your orthopaedic surgeon. The process of making this decision typically begins with a referral by your primary care doctor to an orthopaedic surgeon for an initial evaluation.
How is knee replacement surgery performed?
During knee replacement surgery, the surgeon surgically removes the damaged bone and cartilage of the joint and replaces it with smooth, artificial implants - thereby eliminating painful bone-on-bone contact.
Almost all knee replacement implants consist of a four-part system:
- The tibial (shin) side has two elements and replaces the top of the shin bone. This portion of the implant is made up of a metal tray attached directly to the bone and a plastic spacer that provides the lower half of the new joint's bearing surface
- The femoral (thigh bone) side is a single element that replaces the bottom of the thigh bone and provides the top half of the new joint's bearing surface. This component also replaces the groove where the patella, or kneecap, sits
- Finally, the patellar component replaces the surface of the kneecap, which rubs against the femur. The patella protects the joint, and the newly resurfaced patellar button will slide smoothly on the front of the joint
References
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons website, accessed March 7, 2017: https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00389
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved.
VISIONAIRE
As a patient considering knee replacement surgery, it is important to remember that you have choices.
In our VERILAST◊ Technology section, we discuss how the choice of materials used to make your implant can have a significant impact on your implant's ability to resist wear.
VisionaireHowever, as important as your choice of implant materials is, it's only part of the equation.
After all, no matter how much new technology goes into the creation of your implant, if your implant isn't correctly aligned within your body, implant wear and performance will still be concerns.
For this reason, we developed VISIONAIRE◊ Patient Matched Technology - a system that uses your own MRI and X-Ray images to design and build surgical instruments customized specifically for your unique knee anatomy.
These streamlined instruments potentially offer several patient advantages:
- Less Time in Surgery
- Less Invasive Procedure
- A More Precisely Placed Implant
Because VISIONAIRE Patient Matched Technology uses the data directly obtained by your MRI and x-ray images to map out your knee and establish your body's true alignment, your surgeon will arrive in the operating room with a greater knowledge of your knee.
Your surgeon will also arrive with customized cutting blocks, made from medical grade Nylon-12, that match the exact outer shape and contours of your knee. During pre-surgical work, your surgeon will work with our engineers to determine the exact bone cuts and angles necessary to remove as little bone as possible while still positioning your implant in its optimal location. Potentially, this technology allows your surgeon to digitally perform and adjust your specific knee replacement multiple times before ever making the first incision in your knee.
Important safety notes
Individual results of joint replacement vary. Implants are intended to relieve knee pain and improve function, but may not produce the same feel or function as your original knee. There are potential risks with knee replacement surgery such as loosening, wear and infection that may result in the need for additional surgery. Patients should not perform high impact activities such as running and jumping unless their surgeon tells them that the bone has healed and these activities are acceptable. Early device failure, breakage or loosening may occur if a surgeon's limitations on activity level are not followed.
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved
XLPE
What is XLPE?
What is XLPE or highly cross-linked plastic?As remarkable as OXINIUM◊ Oxidized Zirconium is, it is the combination of the OXINIUM material on XLPE that makes VERILAST◊ Technology.
XLPE is created by altering chemical bonds in the polyethylene we use to create our plastic inserts. By doing so, we are able to create a
 tighter weave at the molecular level, thus reducing the amount of wear experienced when the metal component rubs against it. Perhaps the easiest way to think of it is like a fabric with a higher thread count.
tighter weave at the molecular level, thus reducing the amount of wear experienced when the metal component rubs against it. Perhaps the easiest way to think of it is like a fabric with a higher thread count.Important safety notes
Hip replacement surgery is intended to relieve hip pain and improve hip function. However, implants may not produce the same feel or function as your original hip. There are potential risks with hip replacement surgery such as loosening, fracture, dislocation, wear and infection that may result in the need for additional surgery. Longevity of implants depends on many factors, such as types of activities and weight. Do not perform high impact activities such as running and jumping unless your surgeon tells you the bone has healed and these activities are acceptable. Early device failure, breakage or loosening may occur if you do not follow your surgeon's limitations on activity level. Early failure can happen if you do not guard your hip joint from overloading due to activity level, failure to control body weight, or accidents such as falls. Talk to your doctor to determine what treatment may be best for you.
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved
OXINIUM Total Knee
VERILAST◊ knee technology
Our LEGION◊ CR knee with VERILAST◊ technology was lab-tested to simulate the number of steps the average person takes in 30 years1
OXINIUM◊ + XLPE = VERILAST TechnologyVerilast Knee
If knee replacement is in your future, you've come to the right place to learn about one of the truly significant advancements in joint replacement materials in the past 20 years, VERILAST knee technology.
It's important to remember that not every knee implant is the same. VERILAST knee technology directly addresses one of the most commonly cited concerns associated with knee replacement implants:1
- Implant wear
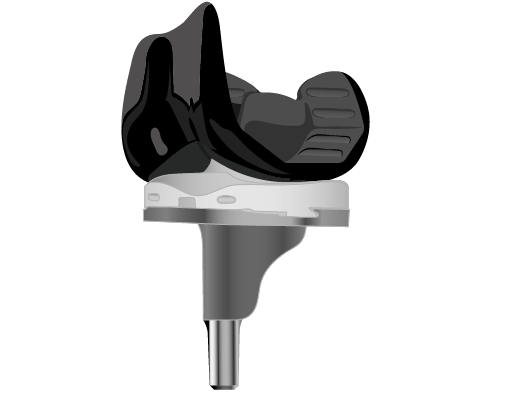
Whether or not to undergo knee replacement surgery is a very important decision. No matter how statistically safe and successful knee replacement surgery has proven to be, every surgery has risks. Before making any surgical decision, conversations should take place with your family, your primary care doctor and your orthopaedic surgeon to make sure that knee replacement with VERILAST Technology is the right course of action for your particular situation.
Important safety notes
Individual results of joint replacement vary. Implants are intended to relieve knee pain and improve function, but may not produce the same feel or function as your original knee. There are potential risks with knee replacement surgery such as loosening, wear and infection that may result in the need for additional surgery. Patients should not perform high impact activities such as running and jumping unless their surgeon tells them that the bone has healed and these activities are acceptable. Early device failure, breakage or loosening may occur if a surgeon's limitations on activity level are not followed.
References
- Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry Annual report. Adelaide: AOA; 2012.
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved.
OXINIUM Partial Knee
Partial knee replacement
Bone and ligament sparing partial knee replacement
Partial knee replacement
Partial knee replacement has been around as a surgical option since the 1970s. Today, partial knee replacement with the JOURNEY◊ UNI knee implant is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that may provide several key benefits to patients whose arthritis is confined to a single compartment of their knee, have a moderately active lifestyle and are within normal weight ranges.
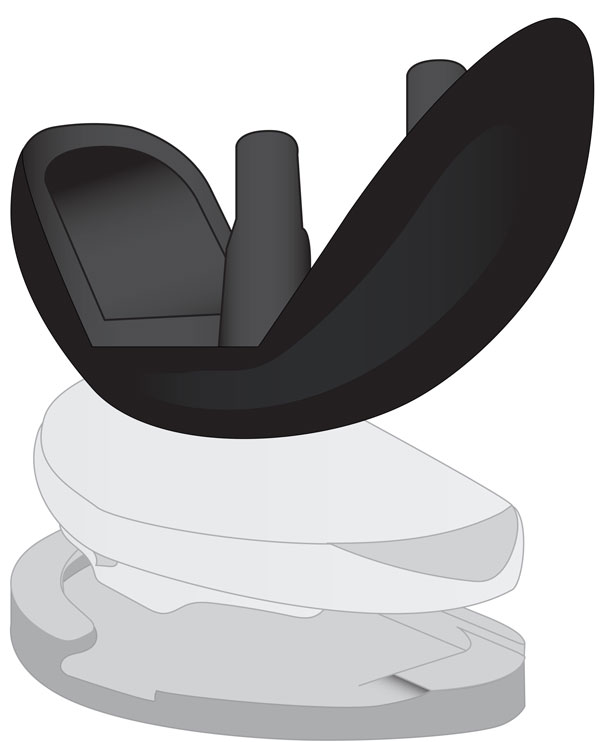

First, let's discuss what is meant by the term minimally invasive surgery or MIS. To be clear, MIS is still a surgical procedure and therefore carries the same risks associated with other surgeries.
However, because it uses specially designed surgical instruments, MIS wth the JOURNEY UNI implant is able to prepare the bones of your knee and then properly place your new implant using a smaller incision than traditional knee replacement. Also, because the implant only replaces one compartment of your knee, there is less bone removed and typically less disturbance to the tissue surrounding the knee than in traditional knee replacement surgery.
According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, partial knee replacement patients usually spend less time in the hospital, have less blood loss, and return to normal activities sooner than do total knee replacement patients. Partial knee replacement patients may also experience better early flexion, less pain after surgery and more natural feeling outcome.
Potential benefits of JOURNEY UNI knee replacement compared with total knee replacement
- No disruption of the knee cap
- Less blood loss
- Possibility for less post-operative pain
- Faster rehab/recovery time
- Better early range of motion
Important: Individual results may vary.
Important safety notes
Individual results of joint replacement vary. Implants are intended to relieve knee pain and improve function, but may not produce the same feel or function as your original knee. There are potential risks with knee replacement surgery such as loosening, wear and infection that may result in the need for additional surgery. Patients should not perform high impact activities such as running and jumping unless their surgeon tells them that the bone has healed and these activities are acceptable. Early device failure, breakage or loosening may occur if a surgeon's limitations on activity level are not followed.
Talk to your doctor to determine what treatment may be best for you.
References
- //orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00585
- Laurencin CT, Zelicof SB, Scott RD, Ewald FC. Unicompartmental versus total knee arthroplasty in the same patient. A comparative study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991; (273):151-156
- Based on the JOURNEY UNI surgical technique
All information provided on this website is for information purposes only. Every patient's case is unique and each patient should follow his or her doctor's specific instructions. Please discuss nutrition, medication and treatment options with your doctor to make sure you are getting the proper care for your particular situation. If you are seeking this information in an emergency situation, please call 911 and seek emergency help.
All materials copyright © 2023 Smith & Nephew, All Rights Reserved

